Tax Saving Investments
Each Indian is legally bound to pay their taxes as per the law made by the Government. The tax amount varies as per the income of the individual/company. But there are varied Sections in the IT Act, which benefit the taxpayers and help them ease the burden of taxes.
Let’s check out some of these tax-saving investments which help in benefiting the taxpayers.
1: Investments Under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act:
This section allows a maximum deduction limit of Rs. 1.5 lakh per year from the taxable income of the taxpayers.
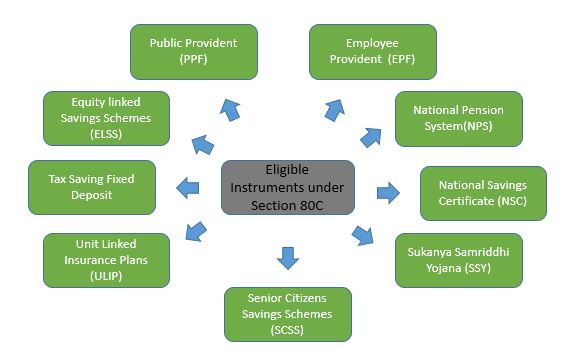
Section 80C is the most desirable and popular section for the taxpayers as it permits the reduction in taxable income by making tax-saving investments.
These Tax Saving Investments include the investments made in:
Public Provident Fund, Equity Linked Saving Scheme, Unit Linked Insurance Plan, SukanyaSamriddhiYojana, National Savings Certificate, Fixed Deposit, Employee Provident Fund, Tax Saving FD, Tuition Fees, Principal Component in Home Loan, etc.
The benefit of these investments can be availed by Individuals as well as HUFs, but the same is not beneficial for companies, partnership firms, and LLPs who are omitted from the same.
-
Public Provident Fund (PPF):
The maximum lock-in period of a PPF investment is 15 years. Post 15 years, you can extend the tenure of investment to 5 more years. Yearly investment in PPF ranging from a minimum amount of Rs. 500/year to a maximum amount of Rs.1.5lac/year is mandatory for keeping the account active.
Partial withdrawal commencing from the 7th year and for each year is permittable.
Your yearly contribution, interest earned as well as proceeds at the time of maturity are all exempt from tax.The maximum lock-in period of a PPF investment is 15 years. Post 15 years, you can extend the tenure of investment to 5 more years. Yearly investment in PPF ranging from a minimum amount of Rs. 500/year to a maximum amount of Rs.1.5lac/year is mandatory for keeping the account active. Partial withdrawal commencing from the 7th year and for each year is permittable. Your yearly contribution, interest earned as well as proceeds at the time of maturity are all exempt from tax.
-
Equity Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS):
ELSS comes with a lock-in period of 3 years and hence is considered to be the lowest lock-in period for tax-saving investments. Taxpayers who are seeking a low lock-in period with a good return on investment can opt for ELSS.
-
Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP):
This financial investment plan has a dual benefit for investors. It provides investment as well as insurance together and hence investors find ULIP investment beneficial. Even long-term goals or other major financial goals can be fulfilled by investing in ULIP. Once the investment in ULIP reaches its due date, the returns earned on the policy are exempt from IT under Section 10(10D).
-
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY):
This investment scheme is initiated by the government for the development of the “girl child”. The main motto of this scheme is to motivate the parents of the girl child to save money for her future expenses like education expenses, marriage costs, etc.
The minimum investment is Rs.250/year whereas the maximum amount is Rs.1.5lac/year. Every quarter interest on the account is added and partial withdrawal is permitted once the girl turns 18 years old.
Exemption of tax on the interest earned on this investment and tax exemption on the entire amount during the maturity period are its positives.
-
National Savings Certificate (NSC):
This investment is initiated by the Indian Government. An investor can approach any Indian post office for opening an NSC account. It guarantees returns just like the PPF account but comes with a lock-in period of 5 years only.
There is no limit on yearly investment in NSC and you will receive the whole invested amount at the end of the maturity period.
-
Tax Saving Fixed Deposits (FDs):
The break-up investments for tax in these FDs is upto Rs.1.5 lac as per Section 80C of the IT Act. These FDs come with a lock-in period of 5 years.
Tax-saving FDs are almost similar to regular FDs with few differences.
You can’t redeem your investments before the maturity date in these FDs whereas the same is possible in regular FDs by paying a penalty. Any Indian citizen can opt for this FD to gain its benefits.
Since the minimum investment is Rs.1000, this tax-saving investment option is suitable for investors who have less to invest and want to gain guaranteed returns. Though the interest amount varies for different banks, the same is taxable.
-
Employee Provident Fund (EPF):
This is the most ideal scheme for salaried people. A contribution of 12% of your salary + dearness allowance needs to be invested in this scheme.
If a company has less than 20 employees, then a rate of 10% is applicable, and for female employees, a contribution of 8% of the salary amount for the first 3 years of working will be sufficient to invest in this scheme.
This amount is deducted by the employer who will add an equal sum of the deducted amount and deposit the same in the EPF.
Your EPF amount + your interest on EPF is tax-free and the same can be withdrawn after 5 years.
-
Tuition Fees:
To promote education for children, the government of India has given ample tax benefits for parents paying educational expenses. This helps in reducing their taxable income.
Tuition fees/education fees paid by parents to schools, colleges, or any other educational institution are eligible for deductions under Section 80C.
A maximum deduction is available for 2 children per individual, i.e., for 4 children for a couple who can claim a deduction upto Rs. 1.5 lac each for every financial year.
-
Principal Component in Home Loan:
An individual is entitled to tax deductions on the amount paid as the principal component of the EMI on the housing loan. A maximum amount up to Rs. 1.50 lakh can be claimed as tax deductions under Section 80C.
The tax deduction is possible only in cases where the individual has possession of the house.
2: Investments under Section 80C, Section 24, Section 80EEof the Income Tax Act (Home Loan Interest):

- Under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, the maximum deduction permitted for repaying the principal amount of a home loan is Rs. 1.5 lakh. The claim is valid for the year wherein the payment is made.
- Under Section 24 of the Income Tax Act, homeowners can claim a deduction upto Rs.2,00,000on the interest paid on home loan. The same is valid only if the owner is residing in the same property. In the case of rental property, the whole interest amount can be claimed as a deduction against the rental income.
- The house owner can claim an additional interest deduction benefit as per Section 80EE subject to fulfilment of conditions as laid down in the said
- In the case of joint application of a homeloan, both the borrowers can avail the tax benefits on their taxable income individually. A maximum amount of Rs.2 lac on the interest paid and an amount of Rs.1.5 lac on the principal amount will be eligible for a tax deduction.
3: Investments under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act (Mediclaim Premium):

Section 80D is all about medical insurance and its benefits to taxpayers. Medical insurance is costly since it requires an individual to pay for the premiums.
Section 80D of the Income Tax Act permits deductions on these medical insurance premiums paid for you and your family.
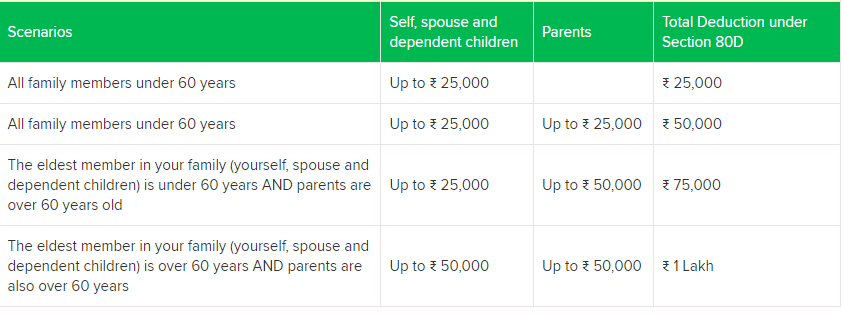
Deductions for the same can be claimed for yourself, your spouse as well as your parents and children.
The deduction under Section 80D is flexible and not fixed and can be claimed by individuals as well as HUF (Hindu Undivided Family). The below-mentioned image clearly states how the deductions under this Section 80D work for varied individuals.
4: Investments under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act (Donation):
The Government of India provides relief to taxpayers who donate or make charities to relief funds and other charitable institutions.
Section 80G of the IT Act, provides tax relief to individuals or companies indulging in humanitarian activities. An individual can claim tax deductions on the donations made by them to trusts and other charitable institutions under Section 80G.
Donations made via cash/cheque are valid whereas made via food, clothing, medicines, etc. are not valid for deduction under this Section. Not all donations can be claimed since there is a prescribed list that qualifies for the same.
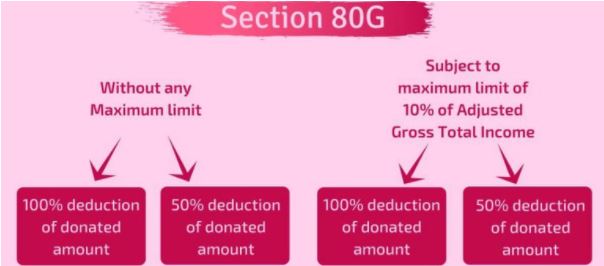
Deduction under Section 80G is restricted to a maximum of 10% of the Gross Total Income and hence there is no fixed deduction amount specified for the same.
Donations made to some trusts are eligible for full deductions whereas some are valid for 50% deductions. You can checkout the same with any CA firm before making the same.
5: Investments under section 80CCD of the Income Tax Act (National Pension Scheme (NPS)):
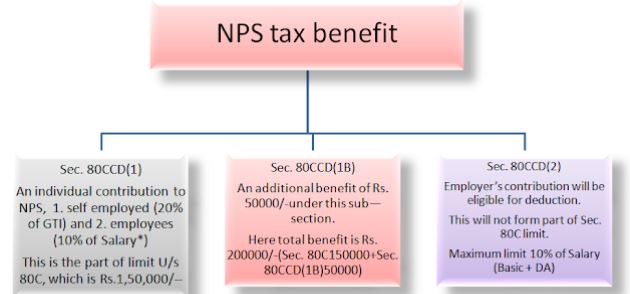
Section 80CCD is all about deductions eligible for individuals making contributions to National Pension Scheme (NPS) or the Atal Pension Yojana (APY). This includes all the employers too who are a part of such investments. This pension scheme initiated by the Central Governmentworks for benefitting all Indian citizens.
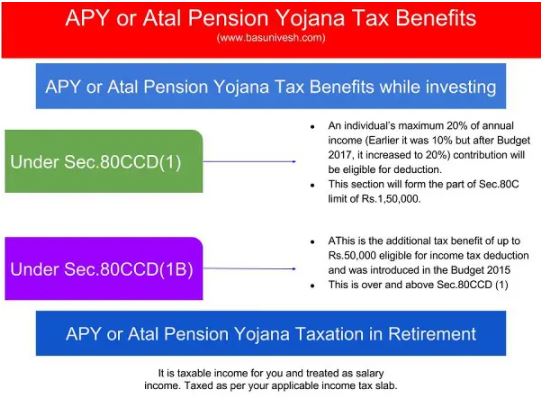
The main motto of this scheme is to ensure a safe retirement for elderly individuals who receive a fixed monthly amount after retiring from their duties. This enables them to live a comfortable life post-retirement.
Wrapping Up:
Wisely investing your money can legally reduce your tax burdens. Plan wisely and start investing at the beginning of the financial year to avoid heavy tax payments.
Choksi Tax Services is the best firm that can effectively and accurately take care of all your taxation issues. Approach them for some wise investments and efficient tax planning.
