An entity is an alliance of two or more individuals who have collaborated to achieve a common business goal.There are varied types of business entities which decides the organization structure as well as the taxes which need to be paid.
Selecting the Appropriate Legal Structure is Essential for Managing your Business.
The foremost step for any business setup is to select the structure of the entity i.e., selecting the type of business entity.
Before selecting a business entity, you should take into consideration the goals of the company, the number of owners, the level of personal risk, company liabilities, registration costs, existence plan, and last but not the least, the taxation costs.
Example:
If you wish to gain total control of your business, a sole proprietorship is ideal, but, if your business involves risk, a LLP (limited liability partnership) is the best choice wherein the risk factor is taken care of.
Study the state and the company laws by considering all the above-stated factors and choose the perfect legal entity for your business. As your business blooms, you can switch the legal structure to another entity as per your business demands and requirements.
In this article, we have penned down some of the most basic types of business entities and their attributes which will help you in selecting the ideal legal entity for your business.
Types of Legal Entities:

1:Sole Proprietorship:
It is the simplest and most basic form of business entity. Since a single owner takes care of the business, he/she is responsible for the profits and losses of the company. You are in total control of the business since you are the boss and all the liabilities linked with the business are your liabilities. The business terminates on the owner’s death.
Since the proprietorship is not taxed as a separate entity, all the gains and losses are stated in the personal tax return of the owner.

2:Partnership Firm:
In this business entity, two or more individuals join together to work and earn profits. The individuals owning the business are termed as partners and their firm is termed as a partnership firm.
In a partnership firm, all the partners contribute money, skill, property, etc.,and share profits and losses as stated in the partnership deed.All the partners are responsible for the liabilities incurred by this firm.
A partnership firm is not a separate legal entity, but it’s easy to create a firm since it has fewer compliances as compared to a company. The maximum number of partners in a partnership firm should not exceed 50 members.
The profits of the firm are taxed at the firm level and is exempt from tax in the partner’s individual tax returns.
3: Private Limited Company:

The company ownership is private in the case of a private limited company. This legal entity is formed by a minimum of 2 members and can extend to a maximum of 50 members
It cannot invite the public or investors for buying the securities, nor can it accept funds from the public. Even the shares of a private limited company are not listed on the stock exchange.
This separate legal entity has an easy exit since it can be easily sold or transferred in part or full to another entity/individual without any interruptions in the business.
4:Limited Liability Partnership (LLP):
A limited liability partnership (LLP) is like a partnership firm but it is registered with a mixture of a partnership, and company. It includes members, individuals, partners, other LLCs, or other foreign entities.
LLP permits partners to limit their liabilities while taking benefits of the flexibilities of a partnership. LLP shields its partners in case of debts arising from personal liabilities in case of unproven business activities.
Minimum two partners are required to incorporate an LLP. However, there is no upper limit on the maximum number of partners of an LLP. This legal entity is ideal for small or start-up businesses.
The profits of the LLP are taxed at the LLP level and is exempt from tax in the partner’s individual tax returns.
5: One Person Company (OPC):
One Person Company (OPC) as the name suggests includes only one member in the company. Usually, companies or partnership firms have a minimum of 2 members, but OPC is formed with only a single member.
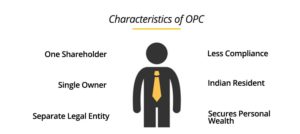
This legal entity is preferred by single individuals, traders, or other small service providers who wish to gain recognition of their identity as well as a business via corporatization. So, in a nutshell, OPC is just like a sole proprietorship, enjoying all the tax benefits of a corporate company.
It is a separate legal entity wherein the director/shareholder is the same person. On the death of the director, the company can be succeeded by the nominee.
6:Section 8 Company/Non-Profit Organisation/Trust:

Section 8 company or a Non-Profit Organisation (NPO) is a company that is created for promoting religion, charity, science, art, etc., or any other objects. The main motto of such companies is that the gains/profits acquired by the company will be again put into promoting the objects of the company. No dividend will be paid to the members of the company.
The provisions of the Company Act, 2013 indicate that registered trusts too can become a member of such companies.
The only difference between a Section 8 company and a Trust is that the company act of Section 8 states provisions related to the foundation of the company with charitable objects, whereas, in the case of a Trust, the same is governed by the Public Trust Act. Section 8 company can have other subsidiary companies too.
Wrapping Up:
Factors like flexibility and complexity of the business, business liabilities, tax structures, capital investment, licenses and permits, other rules and regulations also matter in deciding the type of legal entity preferred for business.
Consider all these options with their pros and cons and checkout which legal entity best fits your business type.
As far as the formation of the entity is concerned or other taxation requirements need to be addressed, approach the taxation experts from Choksi Tax Services (CTS)
Their accounting services and taxation experts can help you in forming an ideal legal entity for your business and guide you in tax compliance by giving tax-efficient suggestions.
