The Indian government had been noticing the arbitrary behaviour of tax officers and the helplessness of taxpayers for quite some time.
Apart from the arrogance and authoritative behaviour, rudeness in communications, absence in maintaining appointments, passing of responsibility to another location, inappropriate monetary demands showing signs of corruption, prejudices and biases, etc. were openly challenged and complained by the tax-payers in during the Tax Administration Reform Commission’s (TARC) stakeholder consultations, which were being held at the five Indian metros.
Need for Faceless Assessment:
Taxpayers used to feel powerlessness against bribe demands made on multiple occasions like, solving an erupted tax scrutiny, or an eligible tax refund, etc. for getting their desired result. The ineffectiveness to solve this situation lead to the birth of the Faceless Assessment Scheme by ShriNarendra Modi’s government.

To motivate honest taxpayers, faceless e-assessment was proposed by the Finance Minister Mrs. Nirmala Sitharaman, in the Union Budget 2019.
What is a Faceless Assessment?
Faceless Assessment as the name specifies, defines the absence of physical interface between a taxpayer and an assessing officer. This option is successful in eliminating all the nasty practices including corrupt behaviour by the tax officers on the taxpayers. The computer picks up taxpayers who need to be scrutinized based on their mismatch in taxes or tax evasions. They are then allocated on a random basis to taxation officials, irrespective of their location.
This fantastic vision of the Prime Minister to launch a faceless assessment in electronic mode has been applauded all over the globe.
The major changes with the launch of this scheme are:
- Faceless Assessments (13th August 2020)
- Faceless Appeals (13th August 2020)
- Taxpayer’s Charter (25th September 2020)
Under the Faceless Appeals Scheme, appeals will be selected and randomly allotted to any tax official across the country. The officer’s identity will remain undisclosed.
A “taxpayer charter” has been adopted by the Income Tax Department, which defines the responsibilities and rights of taxpayers and tax officers. Apart from defining, it also helps gain tax payer’s trust by specifying the commitment of the Income Tax department to provide services to the taxpayers and expectations from the taxpayers to abide and comply with tax laws.
The task of the Income Tax Department includes:
Review of Income Tax Return (ITR) filed by taxpayers + Monitoring their IT pattern.
Based on detailed examination, some cases come under investigation (taxpayers who have failed to submit the ITR) and tax notices are sent to these taxpayers, informing them that their ITR has been raised for scrutiny purposes. This is a complete centralized process wherein cases are selected solely on criteria specified by data analytics and AI (Artificial Intelligence).
How does Faceless Assessment Work?
The sole governing authority for the faceless assessment system is located at Delhi, which is The National E-assessment Centre. The authoritative regional centres are located in Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Pune, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, Bengaluru.
Set up for conducting of Faceless Assessment
CBDT has set up following units/centre for smooth conduct of e-proceedings and has specified their specific jurisdiction, roles and responsibilities.
- National e-assessment Centre (NeAC)
- Regional e-assessment Centres (ReAC)
- Assessment units (AU)
- Verification Units (VU)
- Technical Units (TU)
- Review Units (RU)
National e-Assessment Center (NeAC):
It act as a regulatory committee to implement rules and regulations and monitor ReAC. It also assesses, verifies, modifies and send show-cause notices to the assessee if necessary.
Regional e-Assessment Center (ReAC):
ReAC will be established to implement the actions as informed by the NeAC. The PCIT in charge of NeAC, shall monitor the division to assess regulation and process.
Assessment Unit (AU):
- To facilitate the conduct of e-assessment
- To perform the function of making assessment, including identification of points or issues material for the determination of any liability (including refund) under the Act. It shall provide details of the penalty proceedings to be initiated to NeAC.
- To seek information or clarification on points or issues identified, analysis of the material furnished by the assessee or any other person, and such other functions as may be required for the purposes of making assessment
Verification Units:
To perform the function of verification, which includes enquiry, cross verification, examination of books of accounts, examination of witnesses, recording of statements [Except u/s 133A], and such other functions.
Technical Units:
To perform the function of providing technical assistance which includes any assistance oradvice on legal, accounting, forensic, information technology, valuation, audit, transfer pricing, data analytics, management or any other technical matter which may be required in a particular case or a class of cases, under this Scheme.
Review Units:
RU performs the function of review of the draft assessment order, which includes:
- Checking whether the relevant and material evidence has been brought on record
- Checking whether the relevant points of fact and law have been duly incorporated in the draft order or not
- Checking whether the issues on which addition or disallowance have been discussed in the draft order
- Checking whether the applicable judicial decisions have been considered and dealt with in the draft order
- Checking for arithmetical correctness of modifications proposed, if any, and such other functions which may be required for the purposes of review.
Process of Faceless Assessment:
- Tax notices will be issued by National E-assessment Centre (NEAC) to the taxpayers on their registered email address.
- The taxpayer who receives the notice can reply within a time frame of 15 days.
- A tax officer in the Assessment Unit of the Regional Electronic Assessment Centre (REAC) will be assigned for the case, by the Centre.
- Communication with the taxpayer, regional unit, and verification unit, will be done by NEAC.
- NEAC will receive all unit information of this communication and will send the same to REAC.
- After investigating the information received, the REAC will prepare a draft assessment order, which will again be sent to NEAC.
- The accessee will be given chance to protect his case and after which the fine will be imposed.
Features & Benefits of Faceless Assessment:
Apart from reducing corruption, there are multiple benefits of a faceless assessment scheme. Let’s have a view of some of them.
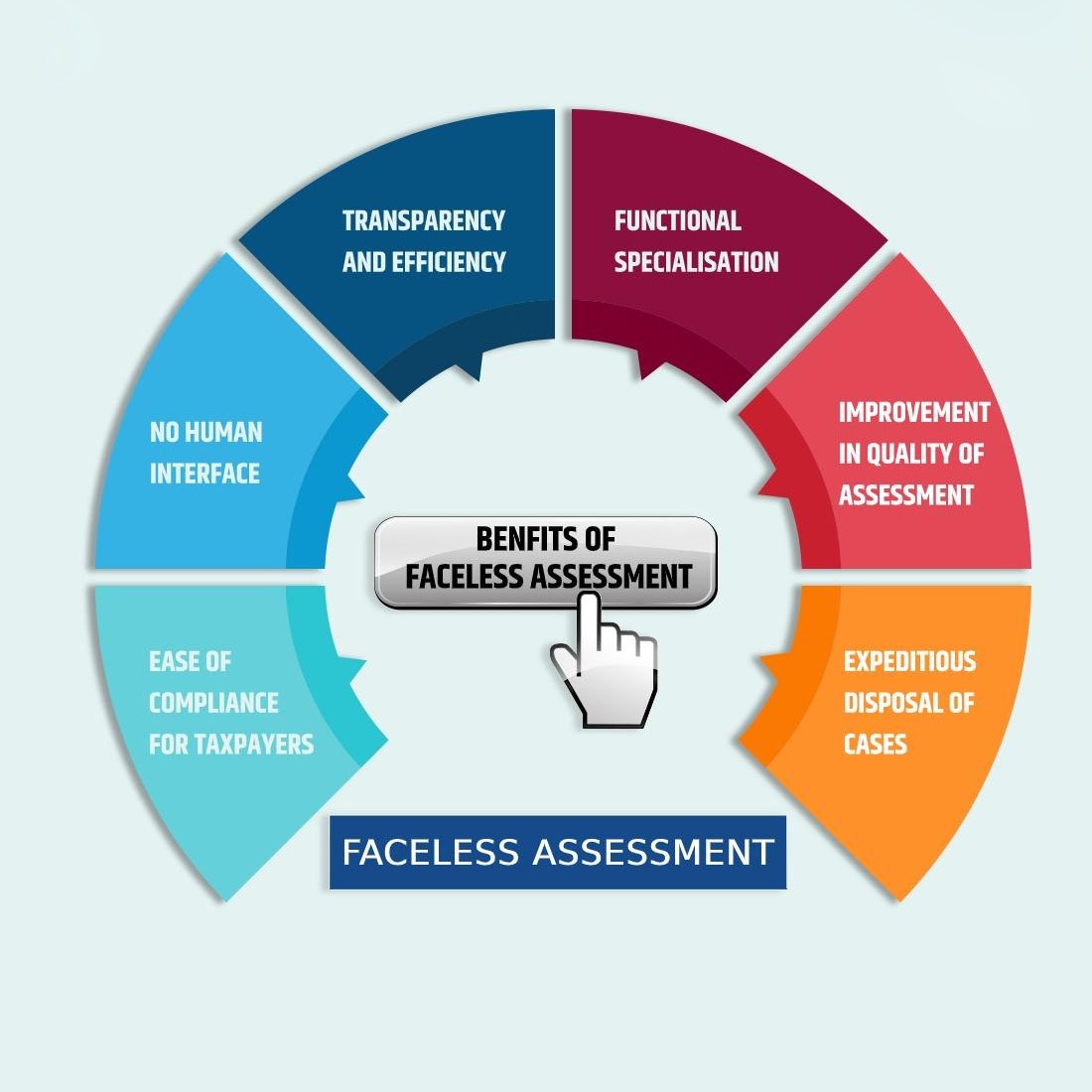
- The assessing taxpayer is selected based on data analytics and artificial intelligence. This rules out the power in the hands of any human – so the chances of error are not there.
- Elimination of territorial authority, i.e. though a taxpayer belongs to X city, assessment is done in Y city, due to random choice of computer.
- Fully automated system and random allocation of cases.
- No presence at the IT office required and no interference from IT officer on a physical basis. So no need for physical visits to IT office.
- Notices are issued centrally with DNI (Document Identification No).
- Draft assessment order, review of the order, and finalization procedure all are done in different cities and hence biased outcomes can be circumvented.
- Fair appeal orders help in minimizing litigation – which is a huge cost both for the assessee and the department.
- Efficiency and transparency in the entire system successfully eradicates corruption and bribery.
- Relief to honest taxpayers. Now the tax payer can complain against the IT officer without any repercussions.
- This digital portal of tax payment can be used any time and any place, irrespective of boundaries.
- Online acknowledgment receipts and transaction ids prove as evidence of tax submission.
- Saves time and effort.
- Cloud Storage and Go Paperless is the future of digitalization and hence India is one of the pioneers in faceless assessment scheme.
Disadvantages of Faceless Assessment:
- Inconvenience in uploading capacious documents.
- Lack of physical demonstration creates difficulty in the explanation process.
- Unexplained tax submissions can lead to wrong decisions and conclusions by tax officials.
- Technical glitches in the online portal may cause a delay in the submission process, leading to penalty charges.
- Restriction in file size (up to 5 MB) and restriction on the number of documents (up to 10 documents) to be submitted on the portal is a major drawback.
How Will Faceless Assessment Impact Business:
Since the Faceless Assessment Scheme has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, the impact of this electronic mode of tax payment is neutralin the business world.
- Since the human interface is excluded in the selection of cases which need to be scrutinized, it will extinct corruption, biased decisions and will give rise to fair judgment, creating a positive impact on business owners as well as their business.
- Taxpayers and assessing officer’s identity tend to remain a secret due to territorial distribution thus creating a positive business environment.
- Taxpayers who do not have the resources or properly equipped system to carry out the task may face a problem. Submission of documents on a technology-based platform, may create hardships for them since loads of documents need to be uploaded on the portal.
- The transition from physical to digital may trigger anxiety in the initial stage. Tax professionals also fret out about the complications that the large enterprises need to face, by uploading loads of documents. Since the upload count is limited, the situation becomes more complex.
Wrapping Up:
The transition from explaining one’s status to an assigned income tax officer physically can trigger agitation while dealing with a faceless system. But there will be a noticeable reduction in the delay in tax assessments and audits because the new assessment system flags unwanted actions.
“Transparent Taxation – Honouring the Honest” platform is indeed an honour to honest tax payers. This digital change helps remove the dark shades of tax officers and reduces the tax litigation burden on taxpayers.
Faceless Assessment Scheme has encouraged the taxpayers for voluntary tax compliance and it is an achievement by itself.
